Effective Communication: Over the years, I've developed strong communication skills through various roles, including IT support, customer service, and organizing student events. Whether I'm explaining technical concepts to users, addressing customer inquiries, or coordinating with team members, I ensure clear and effective communication to facilitate understanding and collaboration.Leadership and Management: As a natural leader, I've taken on roles where I've successfully led teams and managed projects. Whether it's overseeing data migration projects or founding student clubs, I excel in organizing and motivating teams towards common goals. My ability to inspire teamwork and drive projects forward has been instrumental in achieving successful outcomes.
Problem-Solving and Analytical Thinking: With a knack for problem-solving and analytical thinking, I thrive in tackling complex challenges. Through my academic projects in cybersecurity and risk assessment, I've honed my ability to analyze situations, identify vulnerabilities, and develop effective solutions. This skill set allows me to navigate uncertainties and find innovative ways to address issues in diverse professional settings.
Friday, February 23, 2024
My Three Transferable Skills
Friday, February 16, 2024
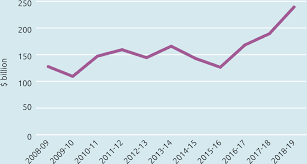
Economic Forecast Analysis for Australia's Automotive Industry
In our endeavor to formulate our annual budget, we are meticulously gathering economic data pertinent to Australia's automotive industry. This entails scrutinizing key indicators such as GDP growth, international trade dynamics, and trends in car sales to inform our budget projections effectively within the Australian automotive market.
GDP Growth Rate: Australia's GDP growth rate is pivotal for gauging the country's economic trajectory and its implications for the automotive sector. By examining historical GDP growth rates, we can anticipate economic shifts that may influence consumer spending patterns and overall demand for cars. A robust GDP growth rate may signify increased consumer confidence and purchasing power, thus impacting our budget allocations for production, marketing, and expansion efforts within the Australian automotive market.
International Trade Volume: Australia's participation in international trade significantly influences our budget forecasts for the automotive industry, particularly regarding car imports and exports. Monitoring trade volumes of cars enables us to assess market dynamics, identify potential trade barriers, and adjust our budget strategies accordingly. Fluctuations in trade volumes may affect import tariffs, supply chain costs, and the overall competitiveness of cars in the Australian market.
Car Sales Trends: Analyzing car sales trends in the Australian market is essential for aligning our budget with consumer demand and market trends. By tracking sales data, we can identify emerging preferences, anticipate shifts in consumer behavior (e.g., growing demand for electric vehicles), and allocate resources effectively. Understanding sales trends enables us to tailor our budget strategies to capitalize on growth opportunities and enhance our market presence in Australia's automotive industry.
Explanation of Graphs:
GDP Growth Rate Graph: This graph illustrates Australia's historical GDP growth rates over the past five years, providing insights into the country's economic performance and its potential impact on consumer behavior and car sales trends.
https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Australia-GDP-growth_fig1_318529289
https://www.dfat.gov.au/publications/trade-and-investment/trade-and-investment-glance-2020
Car Sales Trends Graph: This graph presents sales trends for cars in the Australian market, allowing us to identify patterns and shifts in consumer preferences. By analyzing sales data, we can make informed decisions about inventory management, marketing initiatives, and budget allocation strategies to enhance our competitiveness in Australia's automotive industry.
https://www.dinggo.com.au/blog/car-sales-figures-and-statistics-in-australia
Agile and Waterfall project methodologies
The project management landscape is diverse, with various methodologies available to guide teams in delivering successful outcomes. Two prominent methodologies, Agile and Waterfall, stand out as distinct approaches with different philosophies and practices. Understanding the main differences between these two methodologies is essential for project managers and teams to choose the most suitable approach for their projects.
Waterfall, often considered the traditional or classical approach, follows a sequential, linear process where each phase of the project flows downward like a waterfall. The project progresses through distinct phases, including requirements gathering, design, development, testing, deployment, and maintenance. Once a phase is complete, the project moves on to the next phase, and there is little room for iteration or changes once work has begun. Waterfall is characterized by its structured and predefined nature, with extensive planning done upfront to define requirements and scope before any development work begins. This methodology is suitable for projects with clear and stable requirements, where the end product can be precisely defined from the outset.
In contrast, Agile is an iterative and incremental approach that prioritizes flexibility, adaptability, and collaboration. Agile breaks down the project into smaller, manageable iterations called sprints, typically lasting 2-4 weeks. Each sprint focuses on delivering a potentially shippable product increment, with cross-functional teams working collaboratively to achieve the sprint goal. Unlike Waterfall, Agile allows for continuous feedback, adaptation, and changes throughout the project lifecycle. This iterative approach enables teams to respond quickly to customer needs, market changes, and emerging requirements, leading to faster delivery of value.
One of the key distinctions between Agile and Waterfall lies in their approach to planning and execution. Waterfall relies on extensive upfront planning and documentation, with each phase completed sequentially before moving to the next. This approach is well-suited for projects with stable requirements and predictable outcomes, where changes are costly and disruptive. In contrast, Agile embraces change and uncertainty, prioritizing delivering value early and often. Agile teams focus on working closely with stakeholders, responding to feedback, and continuously improving the product based on changing priorities and market dynamics.
Another significant difference is in the level of customer involvement and collaboration. Waterfall typically involves less customer interaction during the development process, with requirements being defined upfront and changes managed through formal change control processes. In contrast, Agile encourages active involvement of customers and stakeholders throughout the project, with regular opportunities for feedback and validation. This customer-centric approach ensures that the product meets customer needs and expectations, leading to higher satisfaction and value delivery.
Overall, while Waterfall and Agile represent different approaches to project management, each has its strengths and weaknesses depending on the nature of the project and its requirements. Waterfall is suited for projects with stable, well-defined requirements, while Agile is ideal for projects where flexibility, speed, and continuous improvement are paramount. Understanding these differences enables project managers and teams to select the most appropriate methodology and adapt their approach to achieve project success.